Plantar Fasciitis Heel Spur Syndrome
Definition
The plantar fascia is a very thick band of tissue that covers the bones on the bottom of the foot. This plantar fascia can become inflamed (excessive stretching) and painful in some people, making walking more difficult. Risk factors for plantar fasciitis include foot arch problems (both flat foot = pes panus and high arches – pes cavus, obesity, physical activity and tight
Achilles tendon (calf musculature). Plantar fasciitis can affect males and females.
This condition is one of the most common complaints relating to the foot. Plantar fasciitis is
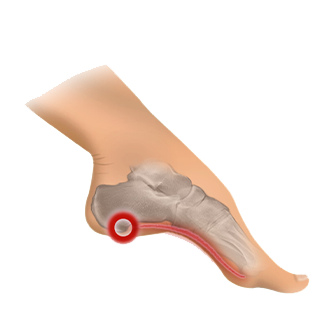
commonly associated with heel spurs. Heel spurs are a bony growth on the anterior aspect of the calcaneus (front of the heel bone). It is the result of prolonged inflammation and tearing of the plantar fascia. On x-ray heel spurs are often seen at the plantar fascia insertion into the heel.
Symptons
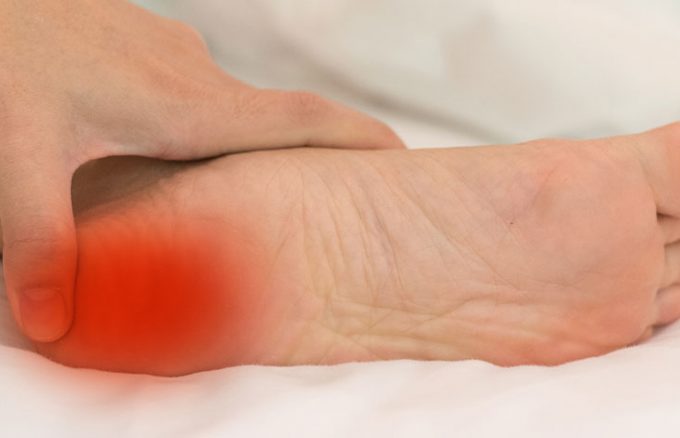
The most common complain is sharp pain in the bottom of the heel (plantar calcaneal area), usually with start up (first thing in the morning) or when standing up or walking for long periods of time.
The sharp pain can be replaced by a dull aching by the end of the day. The pain can be intermittent or constant.
Treatment
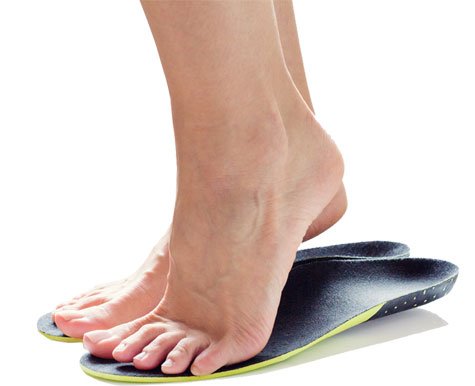
Primarily, the realignment and/or support of the foot if any structural or biomechanical anomalies exist (Innersoles with arch support, prescription orthotics, gel heel cups, supportive footwear).
- Stretching the calf muscles several times a day
- Ice after activity or towards the end of the day
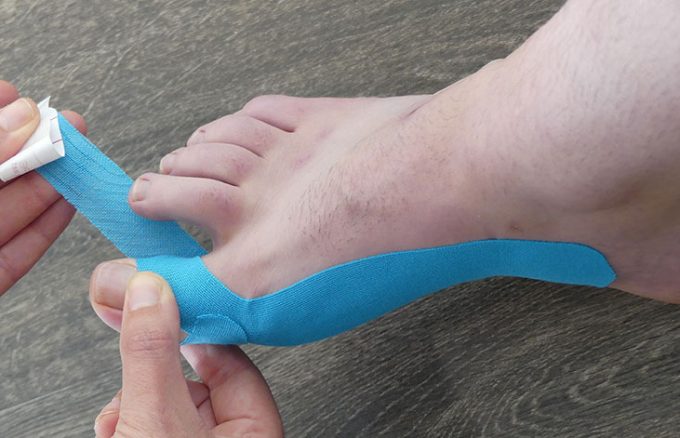
- Taping the foot to provide support and reduce movement
- Altering training regime and levels of physical activity
- Losing weight
- Consulting a Podiatrist/Doctor for specialist medical advice and more detailed treatment options
















Leave a comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.